
Difference Between Anaplasia and Dysplasia Difference Between
114P Anaplasia vs Dysplasia Kevin Mangum, D.O. 36.6K subscribers Subscribe 284 32K views 10 years ago Pathology Visit my website for a full list of videos. Enjoy..

PPT Pathology Lecture Neoplasia PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID8201946
(pathology) Abnormal development of cells or tissue, often a precancerous stage of growth. Sep 02, 2021 Anaplasia Loss of structural differentiation within a cell or group of cells often with increased capacity for multiplication, as in a malignant tumor. Sep 02, 2021 Dysplasia

Difference Between Anaplasia and Dysplasia Difference Between
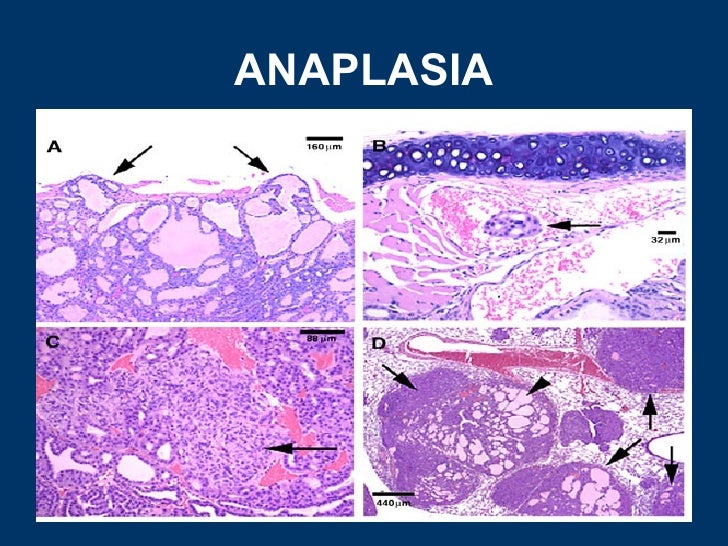
Anaplasia is a term used to describe cells that have lost the unique characteristics that define them as a certain tissue type. In a literal sense from its Greek roots, the word means "to form backwards" in the sense that normal cells become more specialized, not less so, with each division.

neoplasia metaplasia dysplasia Google Search Dibujos de doctoras, Dermatología, Enfermeria
Anaplasia is characterized by insufficient cellular differentiation, whereas cells' aberrant production or development depicts dysplasia. It is called anaplasia, when any alterations occur in the morphological qualities of mature cells and when the cells do not move as a component of the body's tissues.
Perspectiva vela Gladys histology definition anatomy vestido Manto Arancel
As nouns the difference between dysplasia and anaplasia is that dysplasia is abnormal development of cells or tissue, often a precancerous stage of growth while anaplasia is a reversion of differentiation in cells that is characteristic of malignancy in tumours.

Anaplasia vs Dysplasia Meaning And Differences
Overview What is aplasia? Aplasia means that something in your body doesn't develop or work as it should. Many forms of aplasia involve developmental issues present at or before birth. A healthcare provider may notice signs of aplasia, like missing or underdeveloped limbs, in a fetus or newborn.

Anaplasia vs. Dysplasia — What’s the Difference?
Differences: Anaplasia and Dysplasia The following table highlights the major differences between Anaplasia and Dysplasia − Conclusion Anaplasia and dysplasia are two distinct terms that describe different stages of abnormal cell growth.

Différence entre métaplasie et dysplasie Nouvelles 2023
Anaplasia and dysplasia are two types of abnormal cell growth that can occur in cancerous tumors. They are both considered malignant because they can lead to cancerous tumors, but the main difference between these two processes is their rate of progression.

Difference between Anaplasia and Neoplasia YouTube
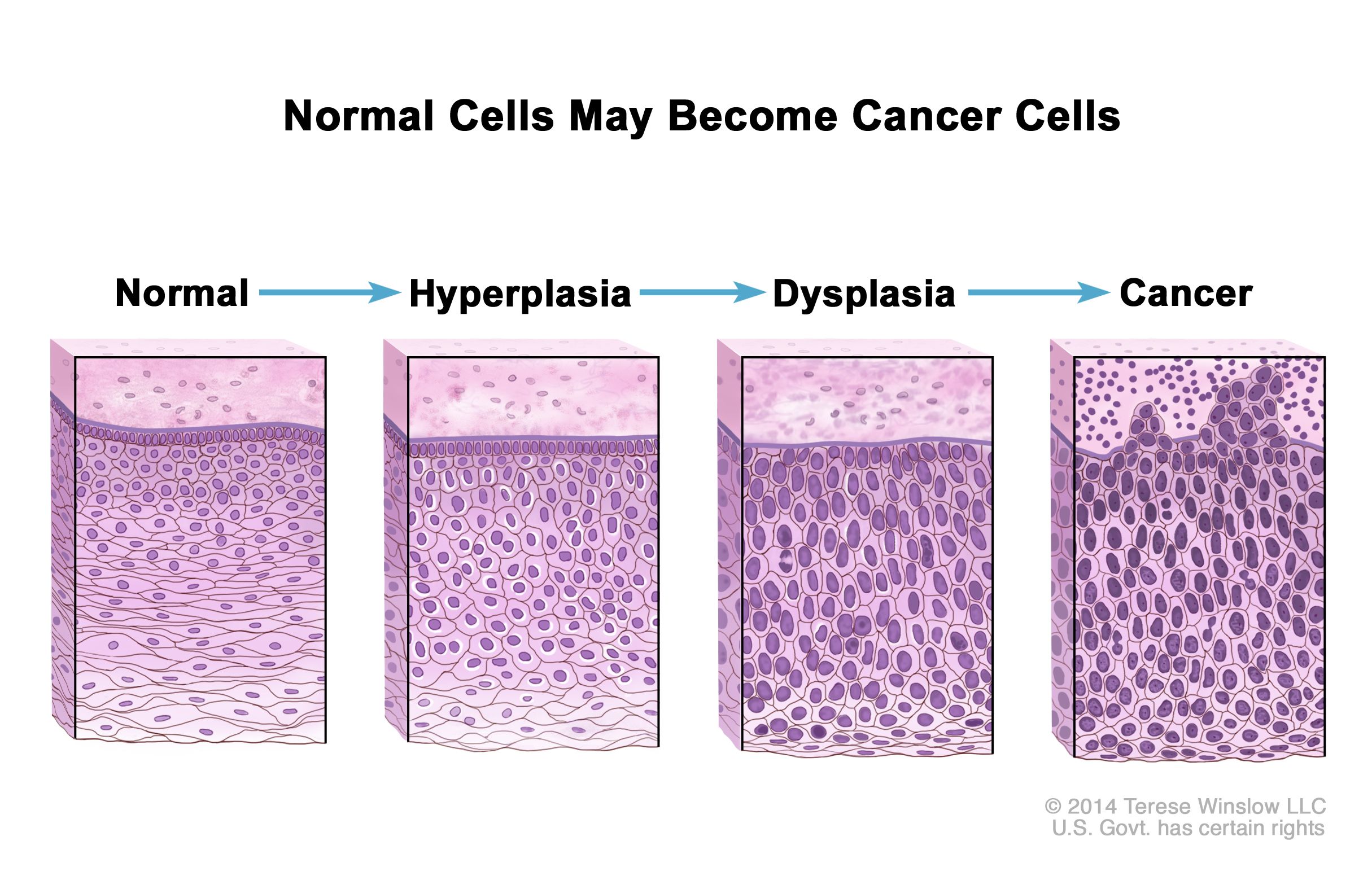
Dysplasia is an increase in abnormal cell growth or development. This is a precancerous state, and it is more serious than hyperplasia, which is just an overgrowth of normal-appearing cells..

2 pathological diagnosis of cancer
Dysplasia is abnormal cells within a tissue or organ. It is not cancer, but it may develop into cancer and is sometimes referred to as precancer. There are also types of developmental dysplasia that can affect different parts of the body. Common types of dysplasia include abnormal growth dysplasia (abnormal growth of cells or tissues that can sometimes be a precursor to cancer) and.

Difference Between Anaplasia and Neoplasia Difference Between
Vs. dysplasia; Summary; Aplasia is a condition in which an organ, limb, or other body part does not develop. In most cases, aplasia is obvious at birth. However, certain types of aplasia may.
What is the difference between dysplasia and anaplasia? Quora
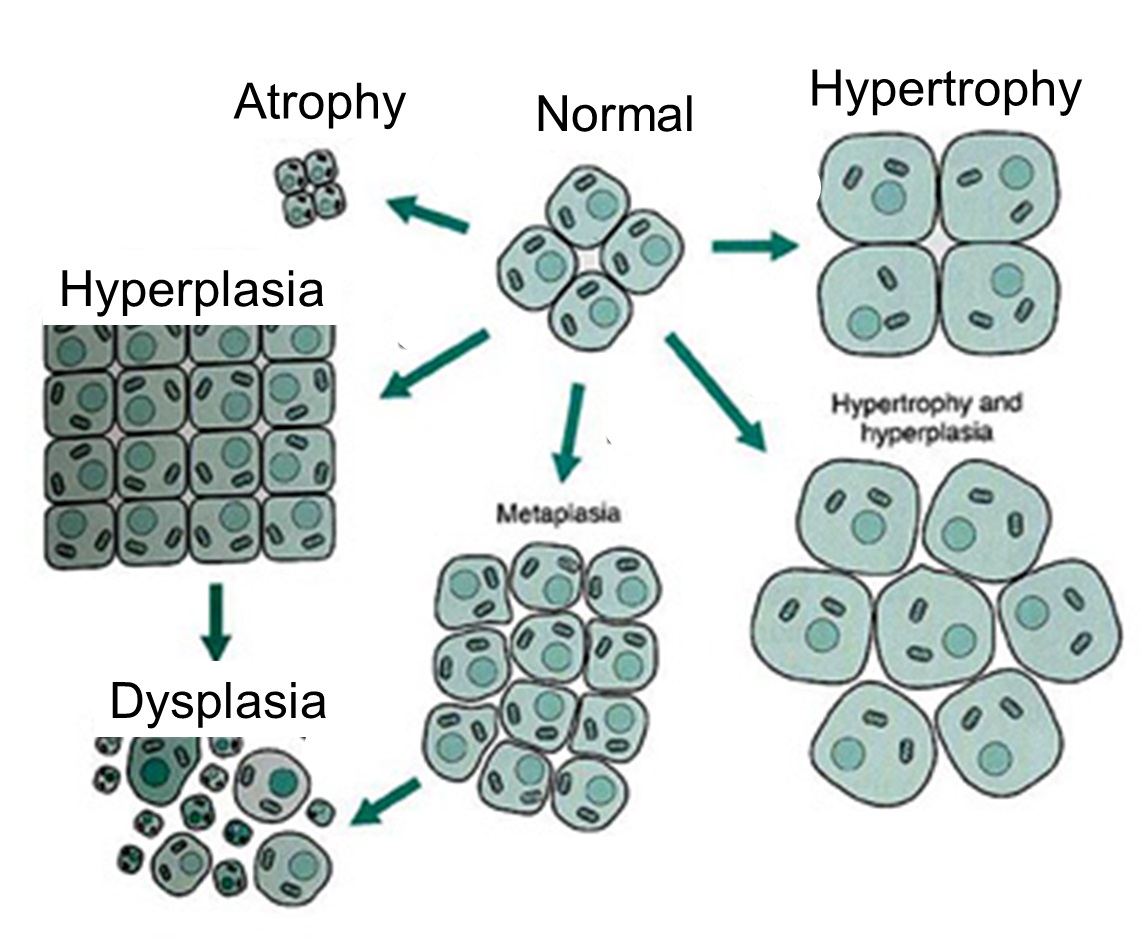
Anaplasia (structural differentiation loss within a cell or group of cells). Aplasia (organ or part of organ missing) Desmoplasia (connective tissue growth) Dysplasia (change in cell or tissue phenotype) Hyperplasia (proliferation of cells) Hypoplasia (congenital below-average number of cells, especially when inadequate)

Displazi Tıpacı
Dysplasia refers to the replacement of one mature cell type with a less mature cell type: for example, dysplasia of the cervix epithelium. Hyperplasia, metaplasia, and dysplasia are reversible because they are results of a stimulus. Neoplasia is irreversible because it is autonomous. Tumor Terminology Generalizations
Lecture Notes in Medical Technology Lecture 2 Mechanism of Cell Damage
Anaplasia refers to the lack of differentiation or maturity of cells; this condition may be seen as irreversible. On the other hand, dysplasia is generally on a less advanced stage as it is seen as a partial loss of mature cells' morphological characteristics. The following discussions further delve into their differences. What is Anaplasia?

MBBS Medicine (Humanity First) Neoplasia Differentiation and anaplasia
alteration of tumours..criterion of tumour formation; (3) anaplasia, or a regression of the physical characteristics of a cell toward a more primitive or undifferentiated type; this is an almost constant feature of malignant tumours, though it occurs in other instances both in health and in disease..a characteristic that is called anaplasia.
General pathology lecture 7 neoplasms
So why is it important to distinguish between anaplasia vs dysplasia? For one, it can help with diagnosis and treatment planning. Anaplastic cells are often indicative of more aggressive cancers, so identifying anaplasia early on can be crucial for determining the best course of action. Additionally, dysplasia can be a precursor to cancer, so.