
CenterTapped FullWave Rectifier Operation … CircuitBread
Power converters with higher efficiency in a wide load range are important for reducing the overall energy consumption of renewable energy generation systems. A center-tapped LC series resonant dual-active bridge (LC-DAB) converter for DC-DC conversion is proposed in this paper. The proposed converter utilizes a center-tapped bridge to block reverse current and eliminate back flow power to.

Center Tapped Full Wave Rectifier Operation Inst Tools
Many people are familiar with bridge full-wave rectifiers but full-wave center-tapped rectifiers are an even simpler way to change AC to a rippling DC. In t.
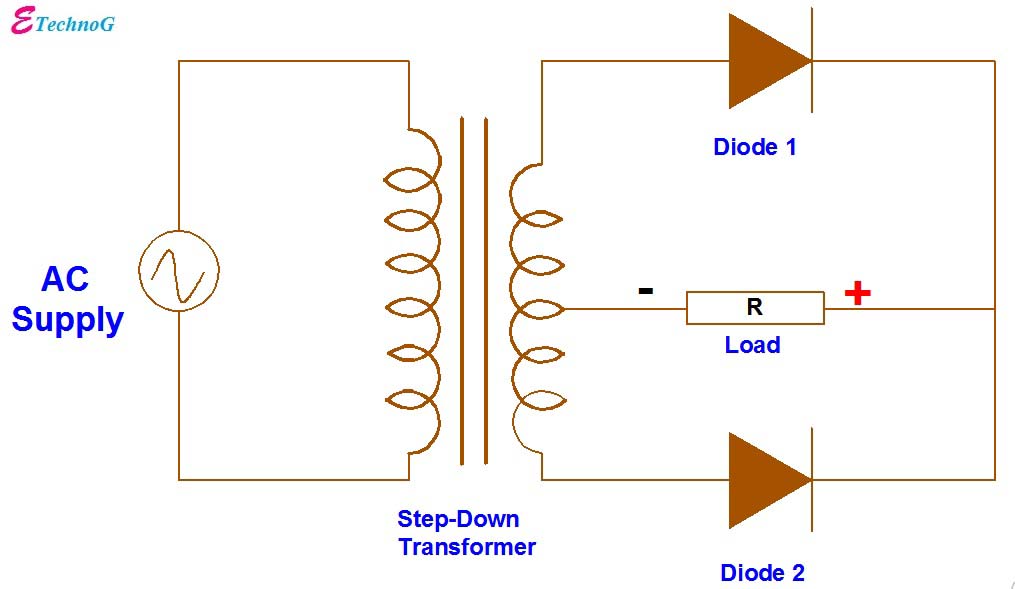
Bipolar Output Full Wave Bridge Rectifier with Center Tapped Transformer. ETechnoG
2 I have a center-tapped transformer which outputs 12V-0V-12V. I was wondering what is the differences between using one full bridge rectifier and two to generate a positive and a negative DC rail. Consider this schematic: It uses one full bridge rectifier and uses the center tap directly as GND.

Full Wave Rectifier Basics, Circuit, Working & Applications
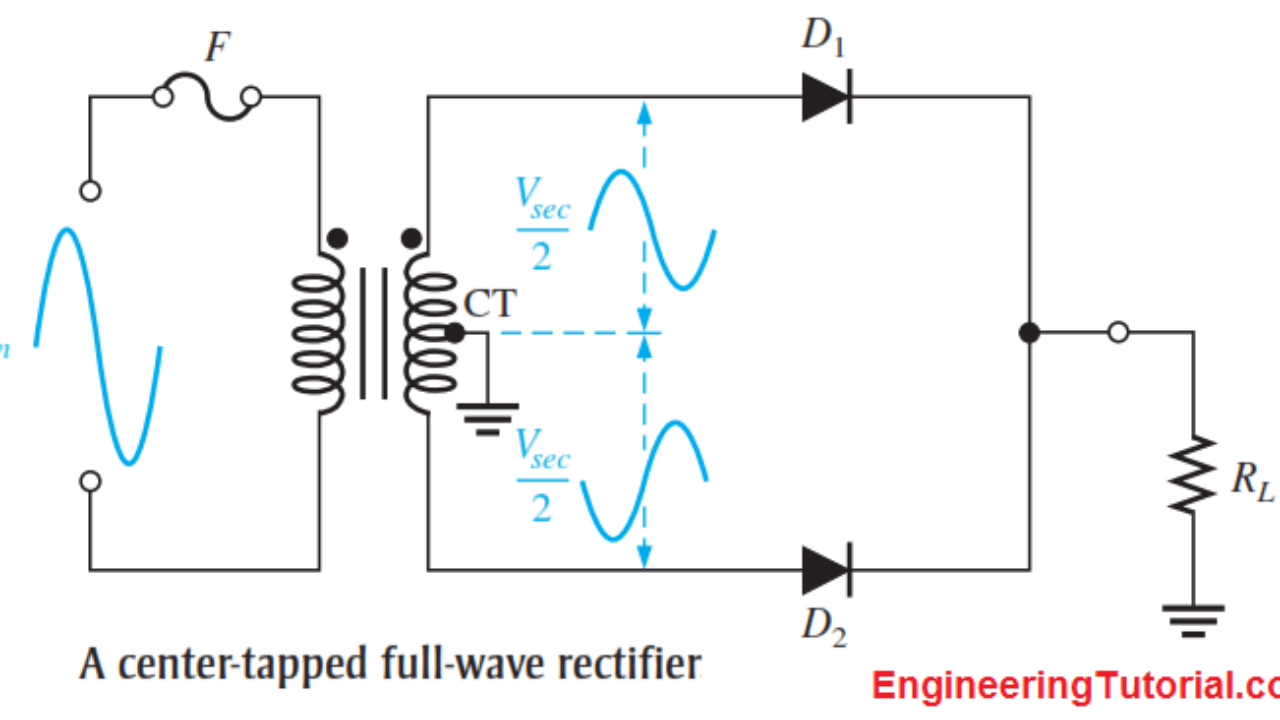
When an additional wire is connected across the exact middle of the secondary winding of a transformer, it is known as a center tapped transformer. The wire is adjusted in such a way that it falls in the exact middle point of the secondary winding. So the wire is exactly at zero volts of the AC signal. This wire is known as the center tap.

⭐ Centertapped and bridge full wave rectifier 😊 Basic electronics. Share this with your friends
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inverter . The process is known as rectification, since it "straightens" the direction of current.
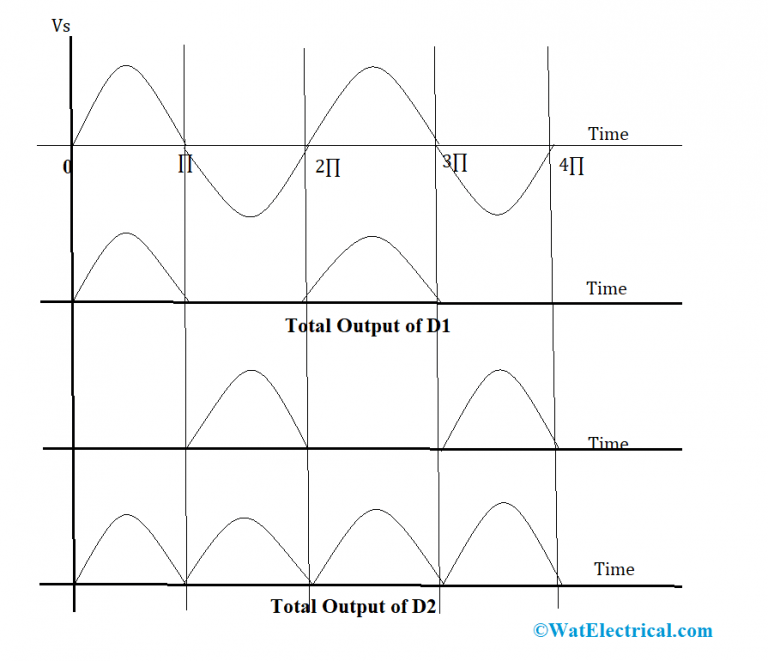
CenterTapped Full Wave Rectifier Definition, Principle & Benefits
The only advantage of bridge rectifier over center tapped full wave rectifier is the reduction in cost. In bridge rectifier, instead of using the center-tapped transformer, four diodes are used. Now we get an idea about the three types of rectifiers. The half wave rectifier and the center tapped full wave rectifier (full wave rectifier) are.

Full wave Rectifier (Center Tap & Bridge) explanation YouTube
One is center tapped full wave rectifier consisting of two diodes and one center tapped secondary winding transformer and the second is a Bridge Rectifier consisting of four diodes namely D1, D2, D3, D4 connected. Types of Rectifiers Working of Full Wave Bridge Rectifier
Difference Between Center Tap Full Wave Rectifier And Bridge Rectifier CrazyEngineers
Centre tapped Rectifier consists of two diodes which are connected to the centre tapped secondary winding of the transformer as well as with the load resistor. Bridge rectifier comprises of 4 diodes which are connected in the form of Wheat stone bridge and thus provide full wave rectification.

CenterTapped FullWave Rectifier Operation … CircuitBread
We can define bridge rectifiers as a type of full-wave rectifier that uses four or more diodes in a bridge circuit configuration to efficiently convert alternating (AC) current to a direct (DC) current. In the next few sections, let us learn more about its construction, working, and more. Table of Contents: Construction Working
Center Tapped Full Wave Rectifier Circuit Diagram Circuit Diagram
This bridge rectifier calculator can assist you in understanding how a bridge rectifier circuit works and how to use one. Bridge rectifiers convert the AC (alternating current) supply voltage to a DC (direct current) supply voltage using four diodes that are ingeniously positioned.

Center Tapped Full Wave Rectifier Full wave center tapped rectifier How to make Bridge
What is Center Tapped Full Wave Rectifier? A type of rectifier which is designed by using two diodes as well as a center tapped transformer for converting the whole AC signal to DC is called center tapped FWR. This is called as "full wave center tapped" because there are two full cycles in one complete cycle of AC voltage.

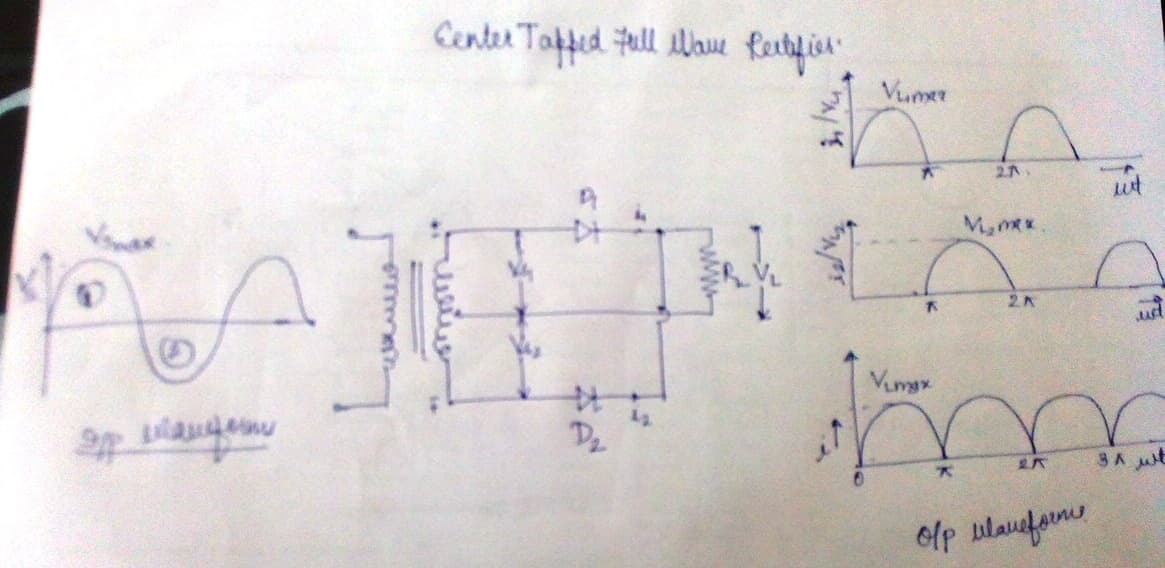
Explain with circuit diagram and waveform working of center tap full wave rectifier.
One of the differences between center-tapped and bridge rectifier is the numbers of diodes used to rectify both positive and negative half-cycles of the AC input. A bridge rectifier uses 4 diodes while a center-tapped rectifier uses only 2 diodes. Triad Magnetics VPS24-5400
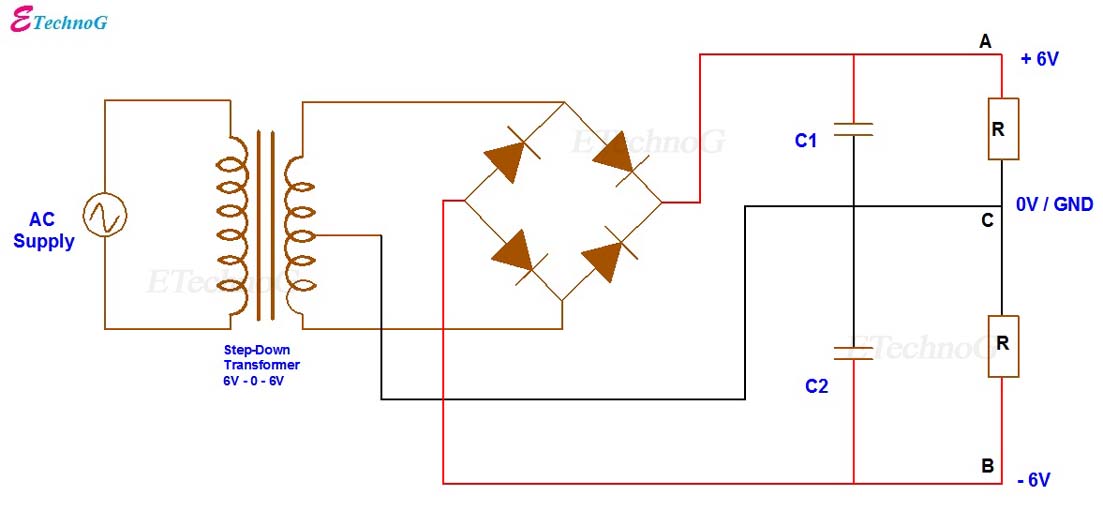
Bipolar Output Full Wave Bridge Rectifier with Center Tapped Transformer. Fundamentals Of
RECTIFIER - Half and Full Wave, Center tap, Bridge. Rectifier is a device which converts the alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and contain one or more diodes. Diode has zero resistance in one direction and infinity resistance in the other direction, so it act like short circuit in one direction and open circuit in other direction.
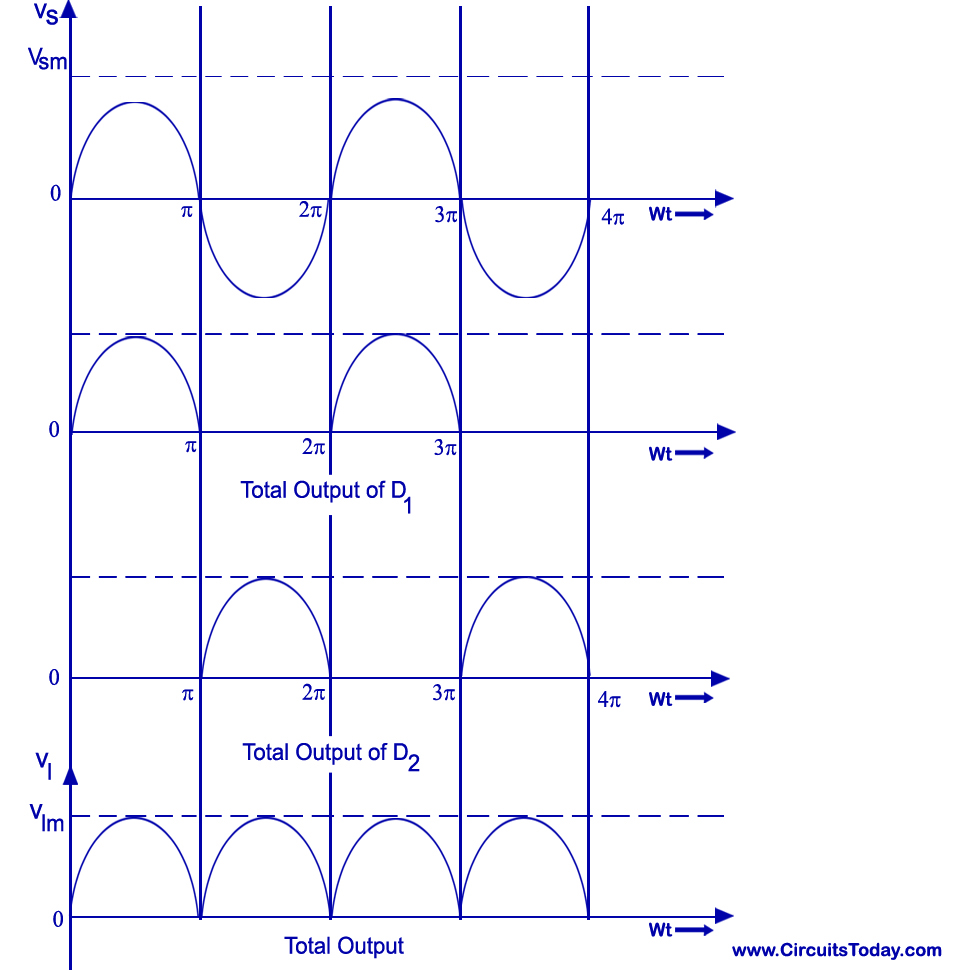
Centre Tap Full Wave Rectifier Circuit operation,Working,Diagram,Waveform
Working of Centre-Tap Full Wave Rectifier. As shown in the figure, an ac input is applied to the primary coils of the transformer. This input makes the secondary ends P1 and P2 become positive and negative alternately. For the positive half of the ac signal, the secondary point D1 is positive, GND point will have zero volt and P2 will be negative.
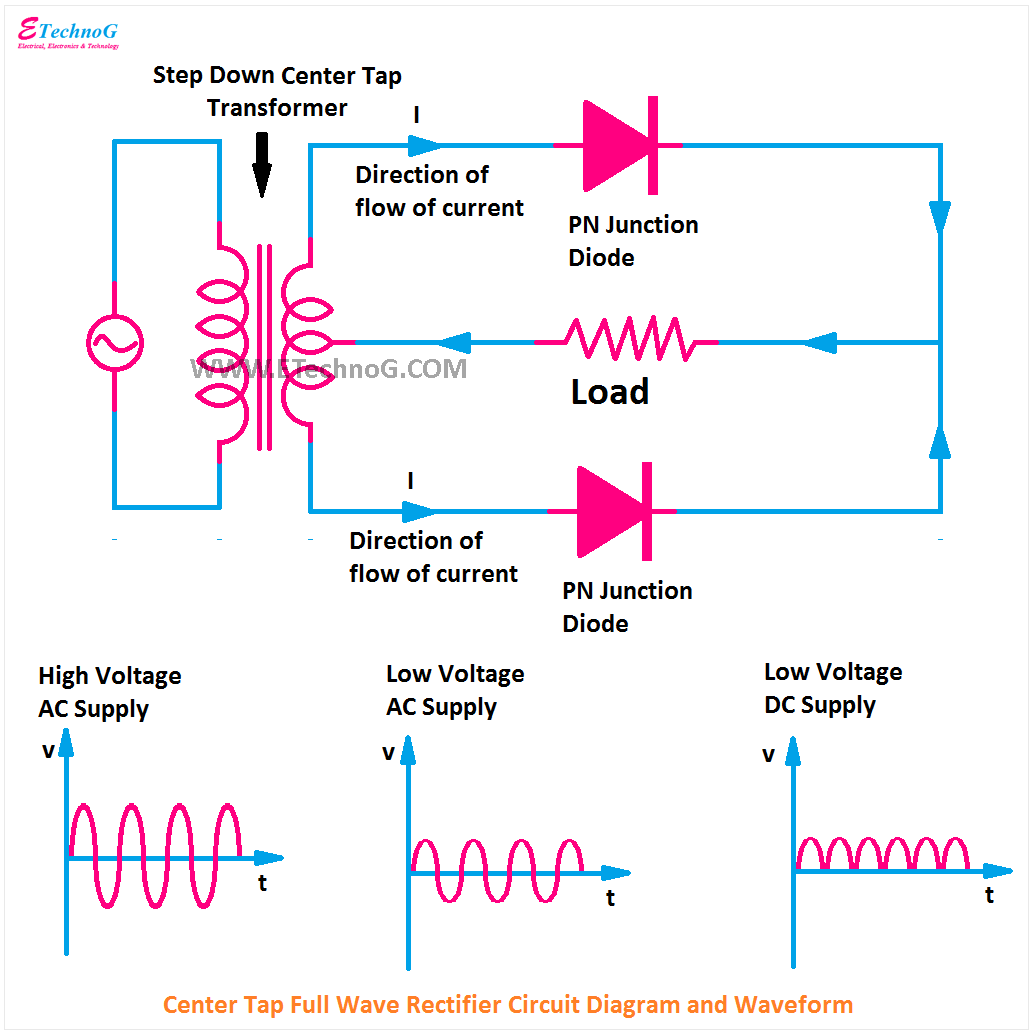
Rectifier Circuit Diagram Half Wave, Full Wave, Bridge ETechnoG
The full-wave rectifier can be constructed in 2 ways. The first method makes use of a centre tapped transformer and 2 diodes. This arrangement is known as Center Tapped Full-Wave Rectifier. The second method uses a normal transformer with 4 diodes arranged as a bridge. This arrangement is known as a Bridge Rectifier.

centre tapped rectifier YouTube
I'm designing a high-voltage power supply for a plasma experiment. I have a center-tapped ignition transformer (50:1) that I'm using to step up the voltage from 120VAC to 6kVAC and then using a full wave bridge rectifier to get +/- 6kVDC. The problem is, the design of the experiment requires me to have 0 and -12kVDC outputs, not +/- 6kVDC.